¶ Introduction
FTS stands for Flight Termination System. Its purpose is to shut down the engine in the event of failure of all previous safety systems, in order to terminate the hopper's flight before it becomes uncontrollable. In addition, the hopper shall be in a safe state so a person can safely come close to it. This means the tanks shall no longer be pressurized.
Several options were considered in order to achieve this function:
- shut down the main avionic. It only works if the entire systeme is designed to be safe in case of a power failure. Moreover, it doesn't close the main valves (as they are actuated by a servomotor), making engine shutdown uncertain.
- adding a solenoid on one or both of the main lines. This guarantees the engine shutdown but the tanks are not depressurized.
- adding a 3 ways valve which would divert the flow from the main valve to the atmosphere. This guarantees the engine shutdown and the tanks are depressurized.
- adding a 3 ways solenoid which would divert the flow from the main valve to the atmosphere. This guarantees the engine shutdown and the tanks are depressurized.
The first two solutions were not keeping as they doesn't meet the requirements. The last two are very similar, only the actuation of the valve change. The last solution was choosen as it doesn't need the development of a custom actuation system with a motor.
¶ Valve
The valve was not easy to find. Three same main problems recurred during the research: the cost, the maximum pressure allowed by the valve and the function of the valve. Indeed 3 ways solenoid valves can achieved different functions and the one needed for this system is not common (see image below)
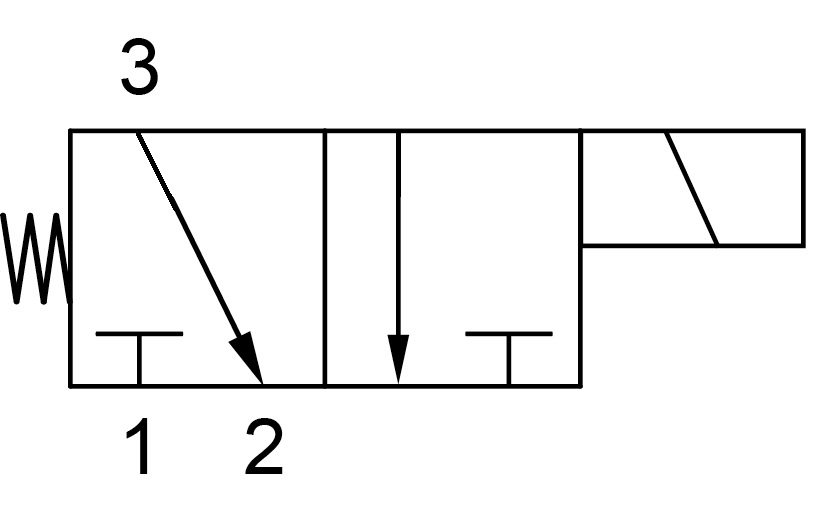
The selected valve is the reference D-DFS3A00HC24B3A from Hydrastore. It meets all the criteria and in addition, it has a very low pressure drop at the fuel mass flow.

It is added on the fuel main line (see plumbing schematic below). When the FTS is triggered, the fuel is diverted to the atmosphere and the oxidizer continues to go to the engine but without fuel, the combustion is immediately stopped. After a few second, both tanks are depressurized. It was chosed that when the valve is not powered, the flow goes to the engine, and to divert the flow the valve has to be powered. This choice was made so that a failure of the FTS would not interrupt a nominal flight.
¶ Electronics
The electronic is divide into 2 parts, on board on the hopper actuating the valve and one board as ground station (GS). Both are completely independent of the main boards to ensure redundancy.
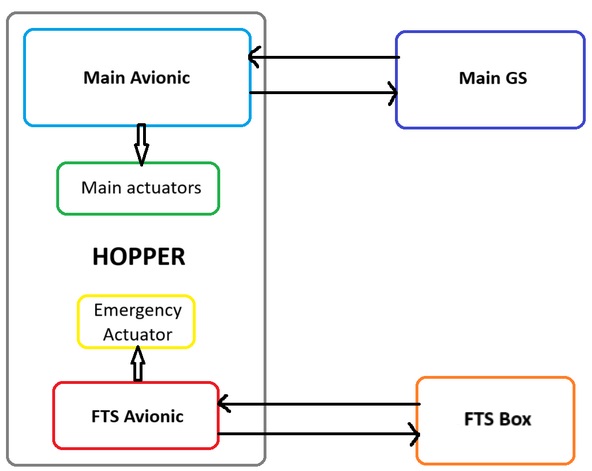
¶ Requirements
The board on the hopper shall:
- actuate the valve
- measure the battery voltage
- have a radio link to the GS board
The GS board shall:
- have a radio link to the hopper's board
- have a switch to trigger the mechanism
- have visual feedback (for example LED) of:
- the status of the GS board (on/off)
- the status of the radio link
- the status of the mechanism (triggered or not)
- low battery on the hopper
- low battery on the GS
Both board shall be powered by a battery for at least TBD [hours].
On the hopper, every FTS components shall be kept away from the main components to prevent any physical failure (battery fire, cable breakage, etc.) from affecting the FTS system as well.